General
eMule is a P2P application which means that many other users will want
to connect to your eMule to upload or download files. For this purpose
eMule opens two ports on which it listens for incomming connections or
packets. If you do not use a router, personal firewall or anything like
this there will be most likely no problem and all incoming packets will
reach eMule, which means that your get a "High ID" (and/or the "Open"
status) and the Porttest will tell your that everything is fine.
If you do use a router, firewall, etc and get a "Low ID" or
"Firewalled" status and the porttest tells you that your eMule is not
reachable, you should configure your router / firewall so that it
allows incoming packets to reach eMule. Please note that eMule does
work with a "LowID" too, but you will have several disadvantages like
slower downloads, because others cannot easily connect to you.
This is a general guide on how to open which ports, but since there are
countless different routers, firewalls and NATs we cannot give you a
step by step instruction for your router or firewall. However in this
section of the help you will find some router models listed with such a
detailed instruction. Also often those instruction can also help for
other models, even if its not excactly the same procedure. If you are
unsure what todo you might want to lookup your router or firewall
manual which often explains how to open ports and together with the
information form this guide, you should be able to give your eMule the
free ports it wants :o)
Using UPnP
Since Version 0.48a eMule supports UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) which
helps to easily configure routers and firewalls which support it. If
eMule is able to setup the needed port forwardings with UPnP on your
router, you don't need to care about port forwardings any further,
because eMule will do all the work for you. To test if UPnP is
available on your system, go to the connection page of the First
Runtime Wizzard (you can restart it with "Tools" => "eMule First
Runtime Wizzard") and click the "Use UPnP to setup ports" button.
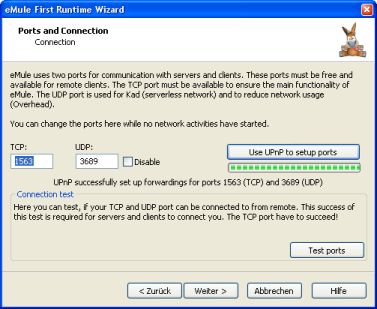
eMule will now test UPnP and tell you if it succeeded or failed. In
case it failed, read the next section to learn how to set up the port
forwardings manually, otherwise you should be finished here. You can
enable or disable UPnP anytime later in the Options => Connections
Dialog.
How to open which ports
eMule listens on two ports, which are randomly selected on the first
start since version 0.47c (earlier version used the portnumbers 4662
and 4672 by default). You can see which ports your eMule has
preselected in the Options menu (see image below). You also can change
those ports if you want to for some reason, eMule is happy with any
portnumber.
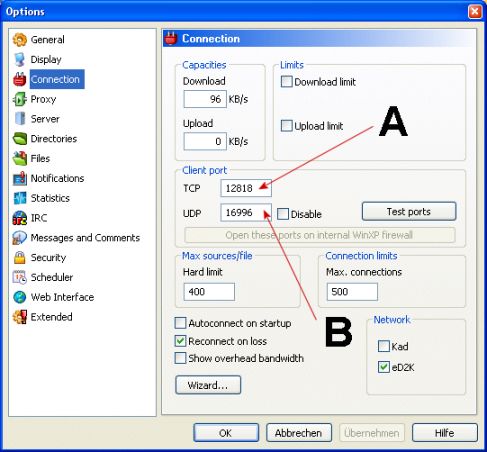
The two ports are marked with A for the TCP and B for the UDP port.
Please note that the actual numbers will be different on your eMule, so
please look them up in your Options dialog and do not take over the
example port numbers from the image. Now you need to open those ports
in the NAT or Port Redirection settings of your router or firewall.
Your will probably find several fields which you need to fill out, the
tables below should help here:
|
Name / Service Name:
|
This is just a name for the rule you can set to whatever you want.
I suggest you use "eMule_TCP"
|
|
Protocol / Transport Type:
|
Select "TCP"
|
|
Public / External Port:
|
Enter your portnumber which is marked with A on the image
|
|
Private / Internal Port:
|
Enter your portnumber which is marked with A on the image (again)
|
|
Direction:
|
Select "Incoming"
|
|
Private / Internal IP:
|
Enter the IP which your PC has in your local LAN (for example
192.168.1.1). Not needed for Personal Firewalls.
|
|
Active / Forward / Enable:
|
Select "Yes" or something similar to enable this new rule
|
And now again for the second port:
|
Name / Service Name:
|
This is just a name for the rule you can set to whatever you want.
I suggest you use "eMule_UDP"
|
|
Protocol / Transport Type:
|
Select "UDP"
|
|
Public / External Port:
|
Enter your portnumber which is marked with B on the image
|
|
Private / Internal Port:
|
Enter your portnumber which is marked with B on the image (again)
|
|
Direction:
|
Select "Incoming"
|
|
Private / Internal IP:
|
Enter the IP which your PC has in your local LAN (for example
192.168.1.1). Not needed for Personal Firewalls.
|
|
Active / Forward / Enable:
|
Select "Yes" or something similar to enable this new rule
|
After adding those rules to your firewall and / or router eMule should
be able to receive incoming connection and therefore get a "High ID".
You can confirm that everything works as intended by clicking the "Test
ports" button. If you still have problems or did not understand any
part if this guide, you might want to try to find help in our forum.
Please do read the guides and helps on this topic first however, since
this is a very common problem.
Optional: Webinterface
If you plan to use the Webinterface to control your eMule from any
computer which is connected to the internet, your will have to include
a rule for this port too. This is completely optional and not needed to
run eMule smoothly. You can find more information about the
webinterface
here. So if you do not plan to use the webinterface, just ignore
this section. Otherwise the following table will help you to open the
default port for the webinterface:
|
Name / Service Name:
|
This is just a name for the rule you can set to whatever you want.
I suggest you use "eMule_Webinterface"
|
|
Protocol / Transport Type:
|
Select "TCP"
|
|
Public / External Port:
|
4711
|
|
Private / Internal Port:
|
4711
|
|
Direction:
|
Select "Incoming"
|
|
Private / Internal IP:
|
Enter the IP which your PC has in your local LAN (for example
192.168.1.1). Not needed for Personal Firewalls.
|
|
Active / Forward / Enable:
|
Select "Yes" or something similar to enable this new rule
|
Additional Note for experienced Users
In very rare cases there might be another port to open: If your router
/ firewall does not supports stateful UDP connections (which means that
it will accept answers to UDP packets you send), you will have to open
a port for the UDP answer packets from servers. This is not needed in
most cases because nearly all routers and firewall do support UDP
answerpackets and even if you are one of the cases where this does not
apply, you will not notice much of it except that sources for rare
files are found a bit slower and Global Server Searches do not work. To
fix this, you will first have to select a fixed port by inserting
"ServerUDPPort=[YourPort]" into the "eMule" section of the
preferences.ini and the open this port in your router / firewall for
incoming UDP traffic.
| 